In the second week of training we started learning about Tableau basics which means a lot of new terminology, rules, and the hardest thing for me to wrap my head around.. date calculations!
I'm sure I'm going to have that magic moment where working with dates just suddenly makes sense to me but here is a little overview of what I understand so far.
Firstly Discrete vs Continuous
Discrete (blue pill) is where dates are separated into individual values for example Jan, Feb, Mar.
And Continuous (green pill) is where dates flow along a timeline.
Date Part vs Date Value
Date Part extracts a part of a date like the month or year for example January or 2026
Date Value keeps the full date but changes its level of detail for example 01/01/2026
Creating Dates in Tableau
1 - TODAY()
Returns the current date which is useful if you want to filter to today's date or compare values relative to today.
2 - NOW()
This is similar to TODAY() but instead of returning the date, it returns both the date and time.
3 - MAKEDATE
This creates a date using year, month, and day values.
MAKEDATE([Year], [Month], [Day])
This is useful if your date data is split across multiple columns or if you're trying to build a proper date field.
4 - DATE
This converts a field into a date data type. For example:
DATE([Order Date])
Which is helpful if Tableau hasn’t automatically recognised a field as a date (kind of related to DATEPARSE in that way).
5 - MAKEDATETIME
This combines separate date and time data fields. For example:
MAKEDATETIME([Date], [Time])
6 - DATEPARSE
This converts a string into a date using a specific format
DATEPARSE("yyyy-MM-dd", [Date String])
*Capital M's are used for months and lowercase m's are used for minutes.
DATEPARSE is useful for when dates are stored as strings or if Tableau isn't picking up the date format.
Add/Subtract Time
7 - DATEADD
This can add or subtract a specific amount of time from a date. For example:
DATEADD('month', 1, [Order Date])
So this calculation would add one month to the order date.
Using a negative number would subtract time instead instead of there being a DATESUBTRACT.
8 - DATEDIFF
This calculates the difference between two dates at a specified level of detail.
DATEDIFF('day', [Order Date], [Ship Date]) - this calc returns the number of days between the two dates, in this case it's the number of days it took to be delivered.
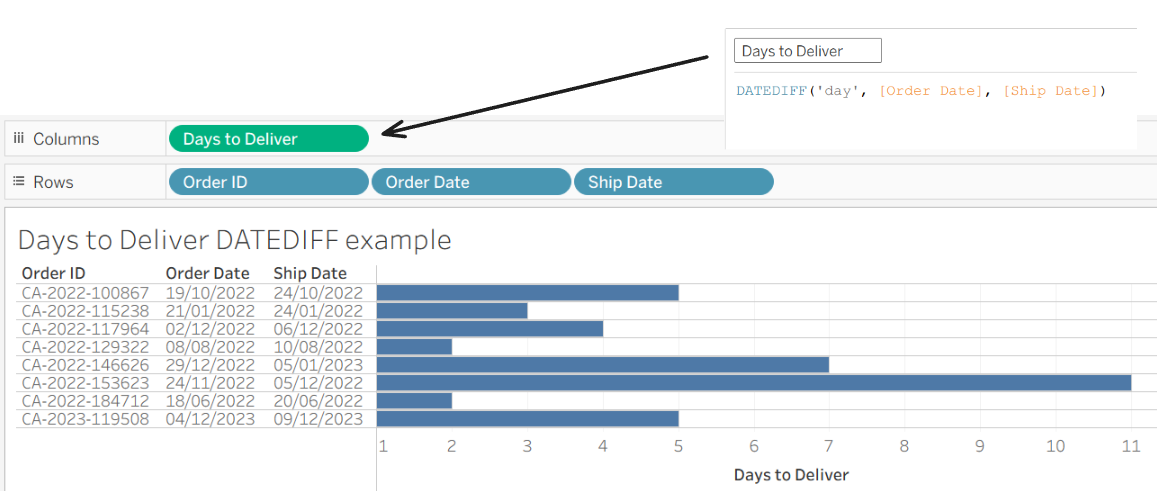
So we can see the top order was delivered in 5 days, and other orders took 2 days and 11 days.
For DATEDIFF you can also use other date parts such as 'week', 'month', or 'year', depending on what you need to measure.
Adjust Dates
9 - DATETRUNC
This truncates a date to a specified level of detail i.e. this rounds a date down to the start of a time period.
DATETRUNC('month', [Order Date])
So this would return the first day of the month for each order date. So for example if the 'Order Date' was 16/03/2026 then it would be rounded down to 01/03/2026.
You could also round by quarter, or year and this calculation is useful for making sure all dates within the same period align to the same starting point. This could then be used to make comparisons such as comparing monthly or quarterly performance - which would make aggregations like sales, counts, or averages a bit easier.
