Tableau Next utilises Semantic Models and Logical Views in order to structure your data.
A Semantic Model is Tableau Next's equivalent of a data model in Tableau Desktop. Here, you can:
- Add, join, and union your tables (by building logical views)
- Form relationships between data objects
- Create calculated fields and parameters
- Define metrics
To create a Semantic Model, click Add in the top-right of your workspace, and select New Semantic Model. Then select the data objects you would like to add to the model, and select/deselect any specific fields you would like to keep/remove.

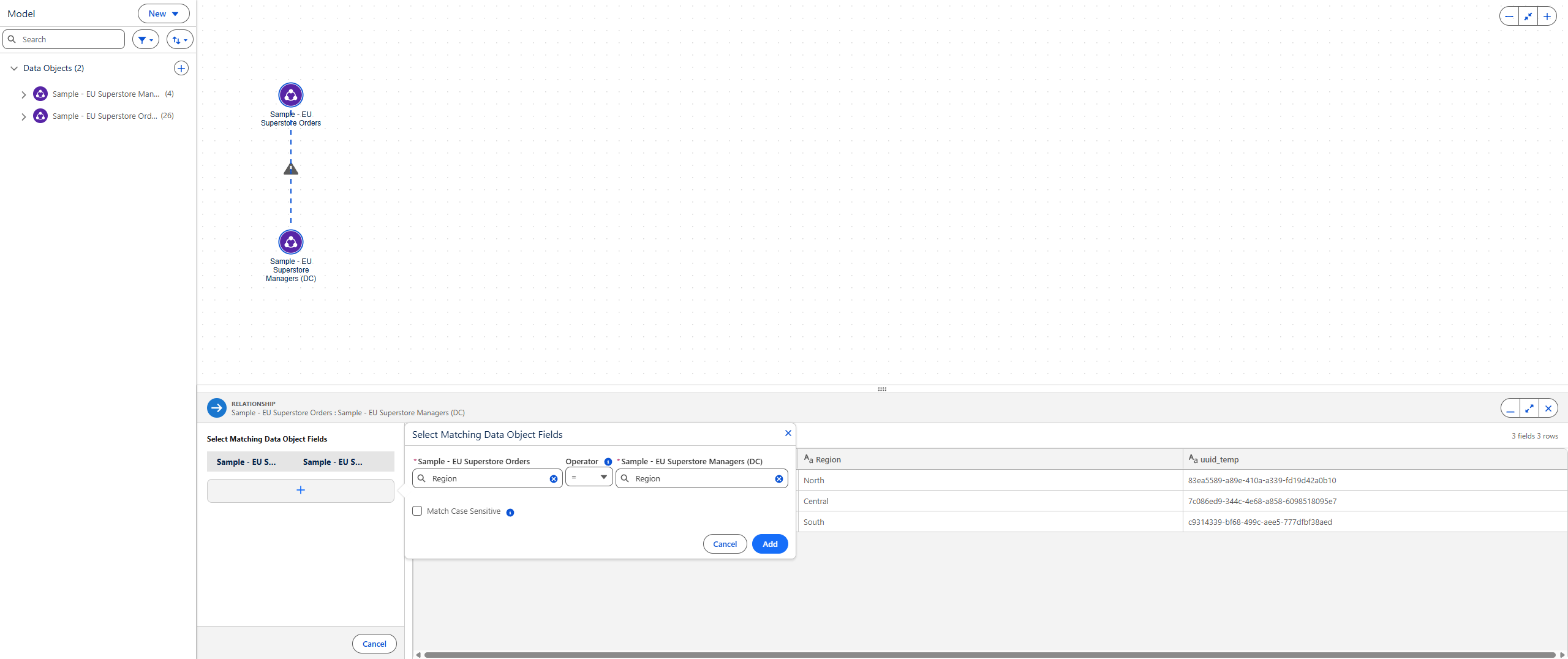
Relationships
Relationships work similarly to Tableau Desktop but are defined in the Semantic Model Builder. You create relationships by choosing related fields (e.g., Order ID in Orders linked to Order ID in Customers), and can add multiple matching fields if required.
Logical Views
A Logical View is a data object composed of multiple tables connected using joins or unions. This lets you create a reusable data object in your semantic model, which you can then create relationships to within the Semantic Model.
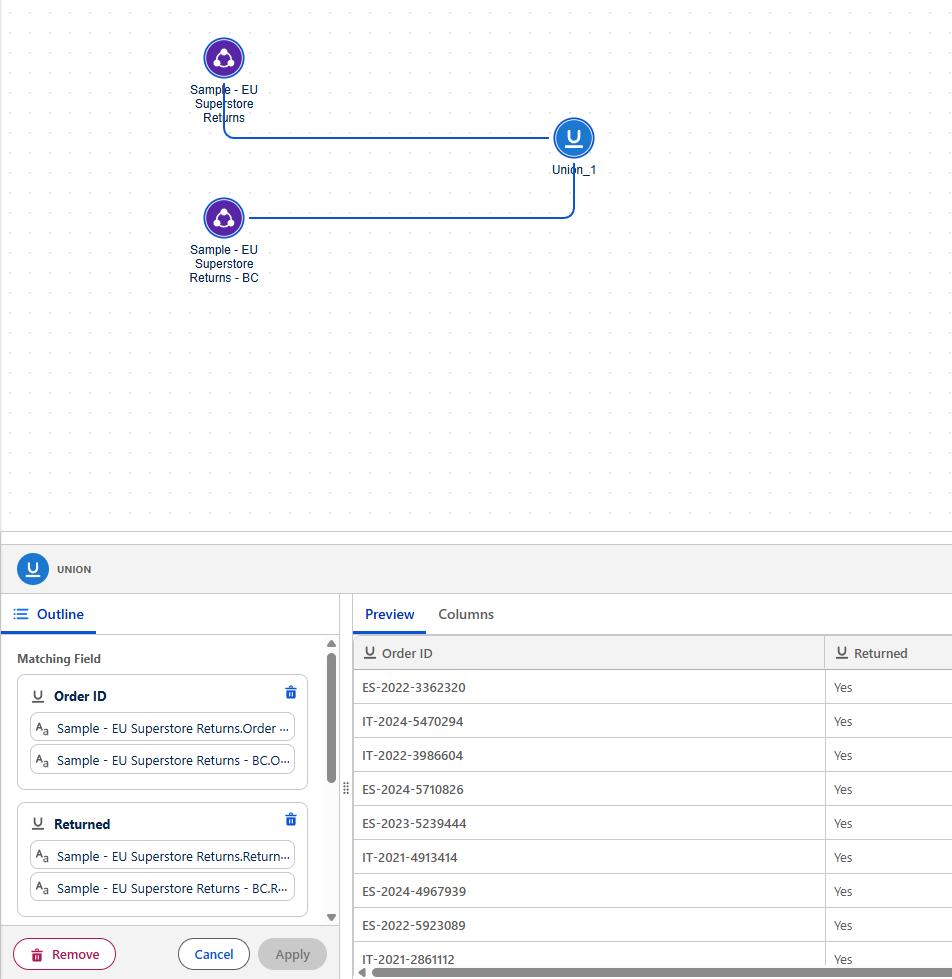

Creating a logical view involves three main steps:
Step 1: Define the Properties
- Open the Semantic Model Builder
- Click to create a new logical view
- Name your logical view (e.g., "Awarded Books")
- Add a description to document its purpose
Step 2: Select Data Objects
- Choose the first data object for your logical view
- Add additional data objects that you want to combine
- Each object you add will become part of the enriched dataset
Step 3: Configure the Logical View
- Define the join types between your data objects (inner, left, right, full outer)
- Select the matching fields for each join
- Configure any additional join conditions
- Review the resulting structure
Once created, your logical view appears as a new object on the Semantic Model Builder Canvas, ready to be used in relationships with other data objects.
Removing Objects from a Logical View
You can remove an object from a logical view, but only if:
- No fields from that object are used in relationships
- The object is not connected via a join to other objects
When you remove an object, any joins between it and other objects in the logical view are also removed.
When to Use Logical Views
Use logical views when you need to:
- Add complicated logic that can't be achieved with standard semantic layer features
- Pre-filter data by combining tables with specific join conditions
- Create reusable data objects that multiple analysts will query
- Simplify complex relationships into a single, easy-to-understand object
Summary
By combining semantic models with logical views, you can encapsulate complex logic, create reusable data objects, and build a semantic layer that makes effective analysis possible for end users.
